192.168.0.1 is a default IP address commonly used by many routers and modems, such as D-link and Netgear, as their default gateway. This IP address is part of the IPv4 address range reserved for private networks, meaning it is not routable on the public internet. Users typically access their router’s management interface by entering this IP address into the address bar of a web browser. From this interface, they can configure various settings such as network passwords, SSID names, security protocols, and more.
How to Login to 192.168.0.1?
To log in to the IP address 192.168.0.1, you typically need to connect your device to the router and then follow these steps:
- Open your preferred web browser (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.).
- Type 192.168.0.1 into the address bar, press Enter, or go to http://192.168.0.1.
- You should be taken to the router’s login page.
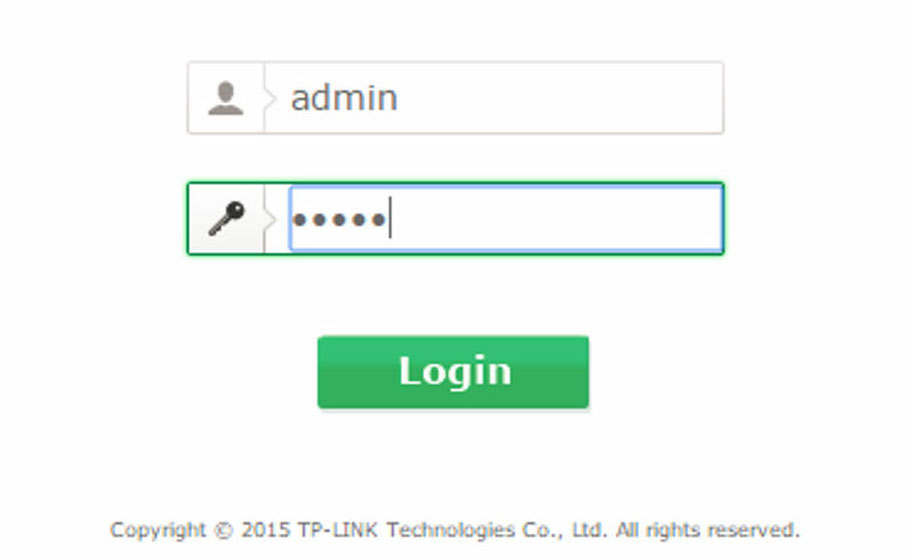
- Enter the username and password. Default credentials are often “admin” for both.
- After that, you will be logged in to your router’s admin panel.
Note: Make sure you’ve typed the IP address correctly; don’t miss it with 192.168.01, 168.192.0.1, or 192.168.0.1.1, and don’t use “https://” or “www” at the beginning. Type the IP address in the URL bar, not the search box.
Forgot Router Login Username and Password?
Check Router’s Label
If you find yourself locked out of your router because you’ve forgotten the username and password, the first step is to check the router for a label or sticker that might display the default login credentials. Many routers come with a default username and password, often something simple like “admin” for both fields. These default credentials can also usually be found in the router’s user manual or on the manufacturer’s website.
Reset Router
If you’ve previously changed the default login credentials and cannot remember them, a more drastic measure would be to perform a factory reset on the router. This process will restore the router to its original settings, including the default username and password. To reset the router:
- Locate the reset button on the router. It is a small, recessed button that may need a paperclip or a tool to press.
- Hold the button down for about 10-30 seconds or until the router’s lights start flashing, indicating it is resetting.
Be aware that this will erase all custom settings, including your Wi-Fi network name (SSID) and password, so you must set up your network again from scratch.
After resetting the router, you can log in with the default credentials and reconfigure your settings. Make sure to write down the new username and password in a secure location so that you can easily access them in the future. Additionally, consider using a password manager to track such credentials securely.
Unable to access 192.168.0.1
If you cannot access 192.168.0.1, there are several potential reasons and troubleshooting steps you can take to resolve the issue.
- Ensure your device is properly connected to the network via Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi.
- Your router may not use 192.168.0.1 but 192.168.1.1. You can easily get it on your computer by opening a command prompt and typing “ipconfig.” The IP address is beside the “default gateway,” which is the address of your router.
- Ensure that your browser does not use proxy settings and that your firewall or antivirus software does not block access to the router’s IP address.
- Clear your browser cache and cookies, then retry.
- Reboot your router and try to access it again.
- Check if your cable is plugged in with your router’s LAN port.
You may need to reset your router to its factory settings if everything fails. This will reverse any changes and allow you to use the manufacturer’s default login credentials.
How to change Router’s WiFi password or SSID?
Changing your router’s WiFi password or SSID (Service Set Identifier) involves accessing the router’s configuration page through a web browser. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Launch any web browser, such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Edge. In the address bar, type your router’s IP address.
- You’ll be prompted to enter a username and password. The default login credentials are often “admin” for both fields, but this can vary by manufacturer.
- Once logged in, navigate to the Wireless or WiFi settings section. This is usually found under a tab labeled “Wireless,” “WiFi,” “Wireless Security,” or something similar.
- Look for the field labeled “SSID” or “Network Name” and enter your desired new name for your WiFi network.
- Find the field labeled “Password,” “Passphrase,” or “Pre-shared Key.” Enter your new WiFi password, ensuring a strong combination of letters, numbers, and special characters for better security.
- After making the desired changes, look for a “Save” or “Apply” button, usually at the bottom of the page. Click it to save your new settings.
After saving the new settings, your router will likely reboot. You must reconnect all your wireless devices using the new SSID and password.
It’s also a good practice to update your router’s firmware to the latest version to ensure you have the latest security patches and features. Most router interfaces have a section where you can check for and apply firmware updates. Updating your router and changing passwords periodically can help enhance your network’s security and performance.
